Introduction:
When purchasing insurance for a car or any other vehicle, people often struggle with deciding between Comprehensive Insurance and Third-Party Insurance. Each option has its own pros and cons and caters to different needs. In this article, we will delve into Third-Party Liability Insurance to address all your questions and concerns.
What is Third-Party Insurance?

Third-Party Liability Insurance, also known as ‘Act-Only’ insurance or ‘Liability-Only’ insurance, is a mandatory requirement for all vehicle owners according to the Motor Vehicle Act, 1988.
Third-Party Motor Insurance is a type of insurance where the insurance company agrees to compensate the insured individual if they are sued or found legally responsible for injuries or damage caused to a third party. Put simply, it’s an insurance policy that shields you from legal responsibilities that may arise in the event of an accident.
For example, if you were to collide with someone else’s car and cause significant damage, your insurer would handle the expenses and/or liabilities resulting from such a situation.
How does Third-Party Insurance work?
To better understand the concept of Third-Party Liability Insurance, let’s clarify some terms using an example of a car accident involving the following parties:
First Party: This refers to the policyholder or the person who has purchased an insurance policy.
Second Party: This refers to the insurer or the insurance company.
Third Party: This refers to the claimant or the person who raises a claim for damages caused by the first party.
If the insured person is found legally responsible for injuries or damages to the third party, the insured is compensated under the Third-Party Motor Insurance Policy (sometimes also referred to as TP Policy). Any losses resulting from damages or injuries caused by the insured to a third party or their property are covered under this policy.
In the event of a car accident, the insured individual with Third-Party Liability Policy must inform the insurer about the incident. If you are deemed responsible for the accident (or the third party believes you are), a claim will be filed against you, which your insurer will be expected to settle.
For a prompt resolution of the claim, it’s crucial to inform the insurance company as soon as possible.
How to claim Third-Party Insurance:
Here’s a detailed explanation of the Third-Party Motor Insurance claim process, including the roles of the First Party (Policyholder) and Third Party (Claimant):
Role of the First Party (Policyholder):
File an FIR: Immediately report the accident to the nearest police station and file an FIR. This documents the incident and establishes a record. Include the following details in the First Information Report (FIR):
- Registration number of the vehicle involved in the accident
- License number of the driver
- Name and contact details of any witnesses present.
Inform Your Insurer: Contact your insurance company as soon as possible and inform them about the accident. They’ll guide you through the claim process and request the necessary documents.
Gather Documents: Collect the documents required for the claim, such as the completed Claim Form, copies of your Driving License and vehicle Registration Certificate, and a copy of the FIR.
Cooperate with Insurer: Assist your insurance company’s surveyor in assessing the damage to the third party’s vehicle or property.
Role of the Third Party (Claimant):
May File a Police Report: The third party may also file a police report about the accident, but this isn’t mandatory.
Seek Compensation: If they wish to recover the cost of repairs or claim for injuries, they’ll need to file a compensation claim with the Motor Accident Claims Tribunal (MACT). They may require legal representation for this process.
Legal Process:
- A lawyer representing the Third Party (claimant) will likely file a case with the MACT.
- The Tribunal will consider evidence from both parties, including the FIR, Surveyor’s Report, and Witness Statements (if any).
- You (the policyholder) may be required to appear before the Tribunal to present your case.
- Based on the evidence, the Tribunal will determine fault and decide on the compensation amount awarded to the third party. (The compensation amount has a maximum limit set by the Tribunal depending on the type of damage (property or injuries).
By understanding these roles and the claim process, you can navigate a third-party motor insurance claim more effectively.
What is covered by Third-Party Insurance?

Property Damage: If you cause significant damage to someone else’s property in an accident, Third-Party Liability Policy covers the costs. This means you won’t have to worry about paying for the damages out of pocket, easing the financial burden in such situations.
Death: If an accident results in the death of a third party, you’re typically liable for the loss. However, with Third-Party Policy, your insurer steps in to handle the financial aspects. Compensation in these cases is determined by court tribunals based on the severity of the loss and the earning capacity of the deceased.
Partial and Permanent Disability: Accidents can also lead to disabilities. Third-Party Policy covers medical expenses for injuries like fractures that can heal over time. In cases of permanent disability, the insurer provides a predetermined sum to the affected party.
Bodily Injuries: Regardless of the severity of a Third Party’s injuries, TP Policy offers medical coverage for all types of bodily harm. This support helps alleviate the financial strain on the insured, recognizing that accidents are unfortunate events beyond their control.
What is not covered by Third-Party Insurance?

Own Damages: Third Party Policy doesn’t cover injuries or damages to the policyholder or their vehicle, whether caused by accidents, fire, natural disasters, or other events.
Driving under the influence of drugs/alcohol: If the driver causing damage to a Third Party was under the influence of drugs or alcohol, the insurance won’t provide coverage.
Invalid Driving License: If the driver doesn’t have a valid license, the insurance won’t apply.
Outside Geographical Limit: If the accident occurs outside the geographical boundaries specified in the policy, no coverage is provided.
Undesignated Driver: If someone other than the designated driver is operating the insured vehicle, Third-Party Liabilities aren’t covered.
Unauthorised Usage: If the insured vehicle is used for illegal activities resulting in Third-Party Liabilities, the insurance won’t cover it.
Keep in mind, that these are common exceptions. For a detailed list, refer to your policy documents.
Importance of Liability Insurance:
Legal Compliance: Third-Party Liability Policy is legally required, ensuring that policyholders meet their legal obligations.
Peace of Mind: While it’s a basic coverage, it provides peace of mind to policyholders, knowing they have financial protection against damages they might cause to others in accidents.
Financial Security: Third-Party Policy safeguards policyholders financially against accidental risks.
Key Features of Third-Party Policy:
- Third-Party Policy provides a fundamental level of protection for all policyholders.
- It covers the policyholder’s Legal Liability to a Third Party resulting from their involvement in an accident. This includes compensation for Personal Injury, Loss of Life, and Property Damage to the Third Party.
- One notable aspect of the Liability Policy is its affordable premium.
However, it’s important to note that Third-Party Policy does not provide protection for the insured car itself.
Private Car Third-Party Insurance Premium:
| Cubic Capicity | Premium |
| Not exceeding 1000 cc | ₹2,094.00 |
| Exceeding 1000 cc but not exceeding 1500 | ₹3,416.00 |
| Exceeding 1500 cc | ₹7,897.00 |
Bike Third-Party Insurance Premium:
| Cubic Capicity | Premium |
| Not exceeding 75 cc | ₹538.00 |
| Exceeding 75 cc but not exceeding 150 | ₹714.00 |
| Exceeding 150 cc but not exceeding 350 | ₹1,366.00 |
| Exceeding 350 cc | ₹2,804.00 |
Access Third-Party Insurance Premium Rates for all vehicle classes. CLICK HERE to download.
Benefits of Third-Party Insurance:
Protection Against Unexpected Costs: In the chaos of daily life, accidents happen. TP Policy ensures that if you accidentally damage someone else’s vehicle or cause injury, your financial burden is lightened. Your insurer will cover these expenses, relieving you of worry.
Legal Compliance: By law, all vehicle owners must have Third-Party Liability Insurance. If you want additional protection for your own vehicle, you can opt for a Comprehensive Car Insurance Policy, which includes coverage for Third-Party Liabilities along with protections for your own car.
Peace of Mind: Knowing that significant financial losses from accidents are covered allows you to drive with confidence. Your insurer will handle expenses, giving you peace of mind on the road.
Legal Support: With Third-Party Policy, you’re shielded from legal issues stemming from accidents. You won’t face court battles if you have valid coverage.
Affordability: Liability Policy is extremely cost-effective. Premiums are tailored to suit all vehicle owners, based on factors like vehicle model and engine capacity. Compared to comprehensive policies, Third-Party premiums are much lower.
Online Convenience: Procuring Third-Party Policy is hassle-free. You can buy Third-Party Policies online through insurance companies’ dedicated portals. Simply log in, explore plans, and select the one that fits your needs.
Disadvantages of Third-Party Insurance:
Absence of Own Damage (OD) Coverage: Third-Party Liability Insurance doesn’t cover damages to your own vehicle. To financially safeguard your vehicle, you need a Comprehensive Motor Insurance Policy.
Limited Add-On Options: When opting for Third-Party Liability Insurance, you miss out on the opportunity to enhance your coverage with various add-ons available with Comprehensive Vehicle Insurance. The basic Liability Policy lacks the flexibility to include additional protections.
Lack of Coverage for Natural Calamities: Unforeseen events like Floods, Earthquakes, or Tsunamis are beyond our control. If your car suffers damage from such natural disasters, Third-Party Liability Insurance won’t offer assistance. Only a Comprehensive Policy covers damages from both natural and man-made disasters.
Penalty for Driving without Insurance:
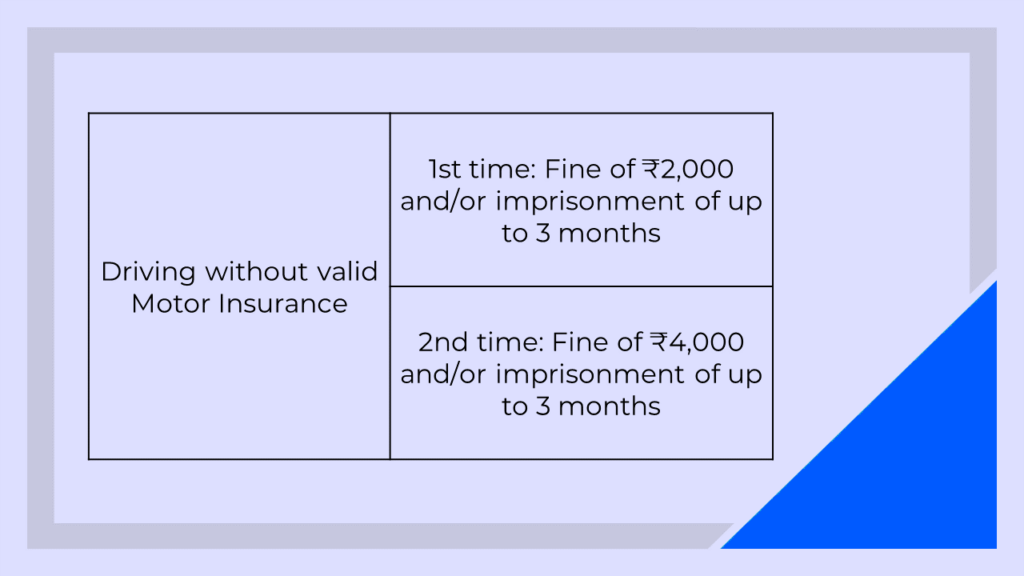
For a comprehensive list of Traffic Violation Fines in India, CLICK HERE.
Comprehensive Insurance vs Third-Party Insurance:
| Comprehensive Insurance | Third-Party Insurance |
| It covers injuries/damages for both the third party and the policyholder. | It covers injuries or damages to only the third party. |
| It is not mandated by law but highly recommended to buy for personal safety and peace of mind. | It is mandated by law. |
| It is costlier than basic Third-Party Libiity Insurance | It is comparatively cheaper. |
| Numerous Add-Ons are available to personalise the insurance policy according to the needs and preferences of the policyholder. | It does not have the option of Add-Ons. |
Resources:
https://irdai.gov.in/document-detail?documentId=1123164
Frequently Asked Questions:
Is Third-Party Motor Insurance mandatory in India?
Yes, indeed. Third-party Motor Insurance is mandatory in India. When purchasing a new vehicle, acquiring a Third-Party Liability Policy is compulsory. As per the Motor Vehicle Act, of 1988, driving a car on Indian roads without valid insurance can lead to severe legal consequences. Therefore, it’s advisable to have at least a Third-Party Policy for your vehicle.
Where can a Motor Third-Party claim be filed?
As per the Motor Vehicles Act, 1988, the affected individual can file a Motor Third-Party claim in a tribunal at any of the following locations: the site of the accident, the residence of the vehicle owner, the location of the involved driver, or the residence of the injured person or their dependents.
What is the highest compensation available for property damage under Third-Party Policy?
The maximum compensation for property damage is ₹7.5 Lac, as directed by the IRDAI. However, the final compensation amount is determined after court proceedings, considering the specifics of the case and in compliance with legal regulations. Applicants must provide the necessary documentation, including a copy of the FIR and original expense records, to validate the extent of the damages.
What is the highest compensation available for injury or death under Third-Party Policy?
In the case of injury or death resulting from an accident, there is no defined limit for third-party coverage. The insurance company assumes responsibility for the total compensation amount once it’s established by the court.
Does the make and model of my vehicle affect the premium of a Third-Party Policy?
Yes, it does. The premium for a Third-Party Policy is influenced by the cubic capacity of the vehicle’s engine, regulated by IRDAI. As different models possess distinct engine cubic capacities, the premiums may differ accordingly.
Can I transfer my Third-Party Policy to the new owner if I sell my car?
Absolutely, you can transfer your insurance policy to the new owner. However, the new buyer must submit an application for transfer of insurance to the insurance company within 14 days of the transfer date. Additionally, the new buyer must pay the endorsement premium for the remaining policy period.
Will I lose my NCB if I claim Third-Party Insurance?
No, making a claim under the Third-Party Liability Policy will not result in the loss of your NCB.
What is the difference between Regular Third-Party Policy and Limited Third-Party Policy?
Regular Third-Party Policy typically provides coverage for damages caused to a third party’s vehicle or property and for bodily injuries or death to third parties. It’s a standard level of protection mandated by law for vehicle owners.
Limited Third-Party Policy, on the other hand, offers similar coverage but with certain restrictions or limitations. These limitations could include coverage caps, specific scenarios where coverage applies, or exclusions for certain types of damages or incidents. Limited Third-Party Liability Policy might be chosen by individuals seeking a lower-cost option or those who believe they have a lower risk of being involved in accidents. However, it’s essential to carefully review the terms and coverage limitations to understand what protection is provided.
Is there any service tax applicable to the Third-Party Policy?
Yes, a standard 18% service tax is applicable to the Third-Party Policy.
What is the duration of the Third-Party Insurance Policy?
The duration of the Third-Party Liability Policy in India for all types of vehicles depends on whether it’s a new purchase or an existing vehicle:
New Vehicles: It’s mandatory to purchase a Long-Term Third-Party Policy valid for 3 years for all new vehicles, regardless of type (cars, two-wheelers, three-wheelers, commercial vehicles).
Existing Vehicles: You can choose between a 1-year policy or a 3-year policy for existing vehicles of any type.
Conclusion:
To legally drive a vehicle on the road, it is mandatory to have a Third-Party Liability Insurance Policy. The Motor Vehicles Act of 1988 requires this coverage to prevent fines. Buying Third Party Policy online is a straightforward process that only requires you to provide the necessary documents and identification proofs.
If you have any questions, please feel free to Contact Us. We are always available to help!
Disclaimer:
This article provides general information only and does not constitute financial advice. Financial regulations, product terms, and industry guidelines are revised from time to time. While we have made efforts to ensure the accuracy of the information presented, we do not guarantee its completeness or accuracy. We disclaim any liability for loss or damage arising from actions taken based on the information provided in this article. To make informed financial decisions, please do your own research and consult with a qualified financial professional.
SPREAD THE WORD WITH YOUR NETWORK

