Introduction:
Investing one’s hard-earned money in Fixed Deposits (FDs) is widely regarded as a secure approach in India. FDs provide a simple starting point for investment and offer attractive returns. Investing in FDs is an excellent choice for individuals seeking to save money, achieve financial objectives, and receive guaranteed returns without assuming risks.
Nevertheless, individuals have limited awareness regarding the functioning of FDs and the precise definition of a Fixed Deposit. Consequently, this article explains the different aspects associated with FDs comprehensively.
What is a Fixed Deposit?
A Fixed Deposit, or FD, is a safe investment choice provided by banks, post offices, and non-banking financial companies (NBFCs) to their customers. To open a Fixed Deposit account, you need to invest a specific amount of money at a fixed interest rate for a predetermined duration. The interest rate can differ across financial institutions, typically surpassing the interest rates offered on savings accounts.
Fixed Deposits are available in various durations, ranging from very short-term periods of 7 days to extended terms of up to 10 years. Sometimes, a Fixed Deposit is also known as a Term Deposit.
How does a Fixed Deposit work?
A Fixed Deposit is similar to lending money to a bank or NBFC. When you invest in an FD, the bank promises to return your investment along with interest at the end of the maturity period. The bank uses this money to lend to others and charges them interest, some of which is shared with you.
The interest rate depends on the FD duration. Shorter-term deposits, like a 7-day FD, offer lower annual interest than longer-term deposits, like a one-year FD. This is because money’s value decreases over time due to inflation. Inflation causes prices to rise, making the rupee worth less in the future. Investors need to be compensated for this.
Different Types of Fixed Deposits:
Getting familiar with the different types of Fixed Deposits offered in the market is crucial to ensure that you make well-informed choice when allocating your funds.
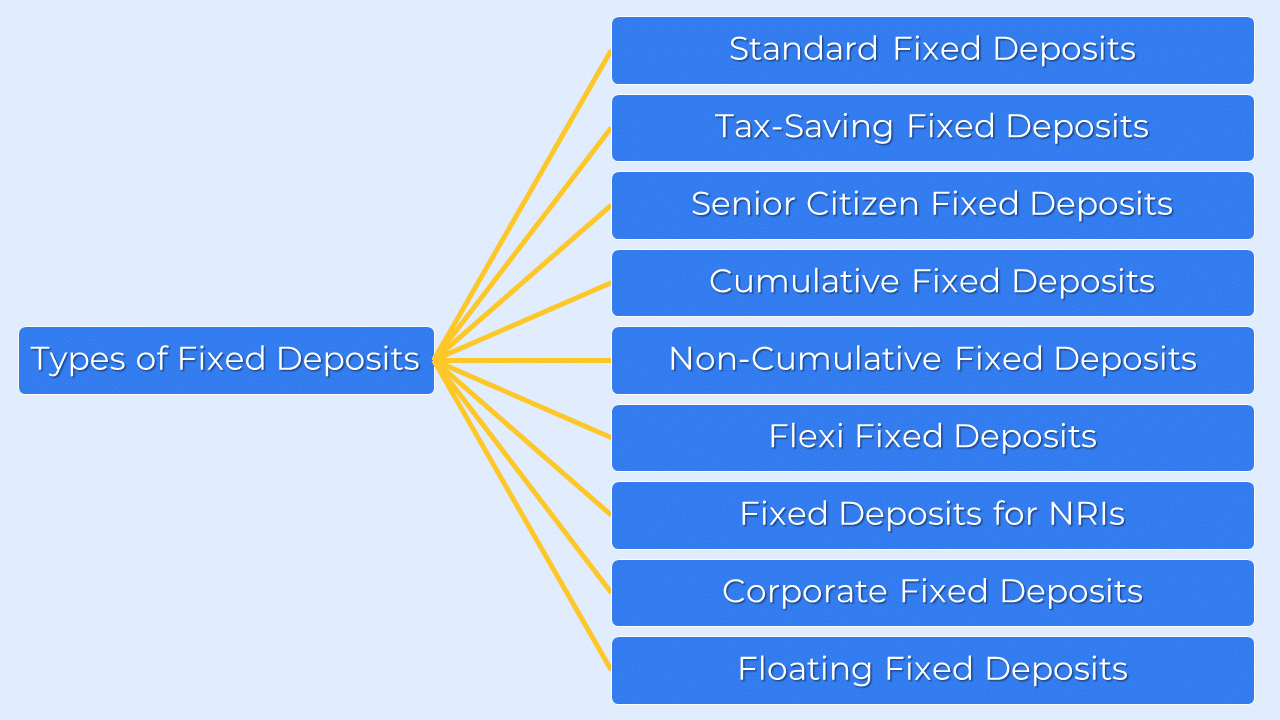
Standard Fixed Deposit:
A Standard Fixed Deposit requires investing money at a predetermined interest rate for a specific duration. The duration of such deposits can range from 7 days to 10 years. This option is widely preferred by most investors.
Tax-Saving Fixed Deposit:
A lock-in period of five years applies to these Fixed Deposits, and they are eligible for deductions under Section 80C of the Income Tax Act 1961. As per income tax guidelines, you can claim a maximum deduction of up to ₹1,50,000 per year.
Senior Citizen Fixed Deposit:
Banks and NBFCs offer higher interest rates on FDs for individuals aged 60 and above, typically providing an additional 25-50 basis points (0.25-0.50%). Senior citizen FDs also come with an extra tax benefit. If the interest earned from these FDs does not exceed ₹50,000 per year, it is not subject to tax deduction at source.
Cumulative Fixed Deposit:
Cumulative FDs provide both the interest and principal amount at maturity. The interest earned is reinvested each year, which means you won’t receive regular interest payouts but instead a lump sum at the end of the FD tenure. This option is suitable if you don’t require a regular income stream. Additionally, with the cumulative FD, you can benefit from the power of compounding, as the interest for the following year is calculated based on the principal amount plus the interest from the previous year.
Non-Cumulative Fixed Deposit:
Non-Cumulative FDs offer regular interest payments at fixed intervals. You can choose from Monthly, Quarterly, Half-yearly, or Annual interest payouts based on your preferences. This ensures a consistent income stream. However, the drawback of non-cumulative FDs is that you won’t earn interest on interest.
Flexi Fixed Deposit:
A Flexible Fixed Deposit is directly linked to your savings account. With this option, you can instruct your bank to automatically transfer any amount exceeding a predetermined balance to a fixed deposit using the auto sweep-in feature. For example, if you aim to maintain a monthly balance of ₹25,000/-, any surplus will be moved to an FD. Conversely, if your balance falls below ₹25,000/-, the bank will withdraw a portion of your FD to maintain the desired balance. This provides the advantage of both liquidity and investment.
The interest rate on Flexible Fixed Deposits is higher than savings account interest rates but lower than Standard Fixed Deposit rates.
Fixed Deposits for Non-Resident Indians:
Non-resident Indian (NRI) citizens can invest in either non-resident external (NRE) or non-resident ordinary (NRO) Fixed Deposits. NRE FDs are ideal for individuals earning in a foreign currency. The major benefit of NRE FDs is that the entire amount, including the principal and interest, is tax-free. On the other hand, NRO FDs can be held in Indian or foreign currency and are subject to a 30% annual tax.
Corporate Fixed Deposit:
Specific companies or corporate entities provide Fixed Deposits as well. Although they offer higher interest rates compared to banks and NBFCs, it’s important to note that corporate FDs come with higher risks. Unlike bank and NBFC deposits, corporate fixed deposits do not enjoy backing and insurance coverage from the DICGC. This means that if a company goes bankrupt, there is no guarantee of recovering your funds invested in corporate deposits.
Floating Fixed Deposit:
In a Floating Fixed Deposit, the interest rate can change every quarter or year based on the Reserve Bank of India guidelines. This allows people to take advantage of the varying interest rates.
Features of Fixed Deposit:
To gain a clear understanding of Fixed Deposits and determine their suitability for you, it’s important to be aware of their key features:
- Adding funds to your existing Fixed Deposit account is not possible. If you have surplus funds to invest, you will have to open a new Fixed Deposit account separately.
- Fixed Deposit interest rates are generally higher than those offered by savings accounts.
- The duration of Fixed Deposits can range from 7 days to 10 years.
- Renewing a Fixed Deposit is a hassle-free process.
- The account holder may need to pay a penalty in case of premature withdrawal.
Benefits of Fixed Deposit:
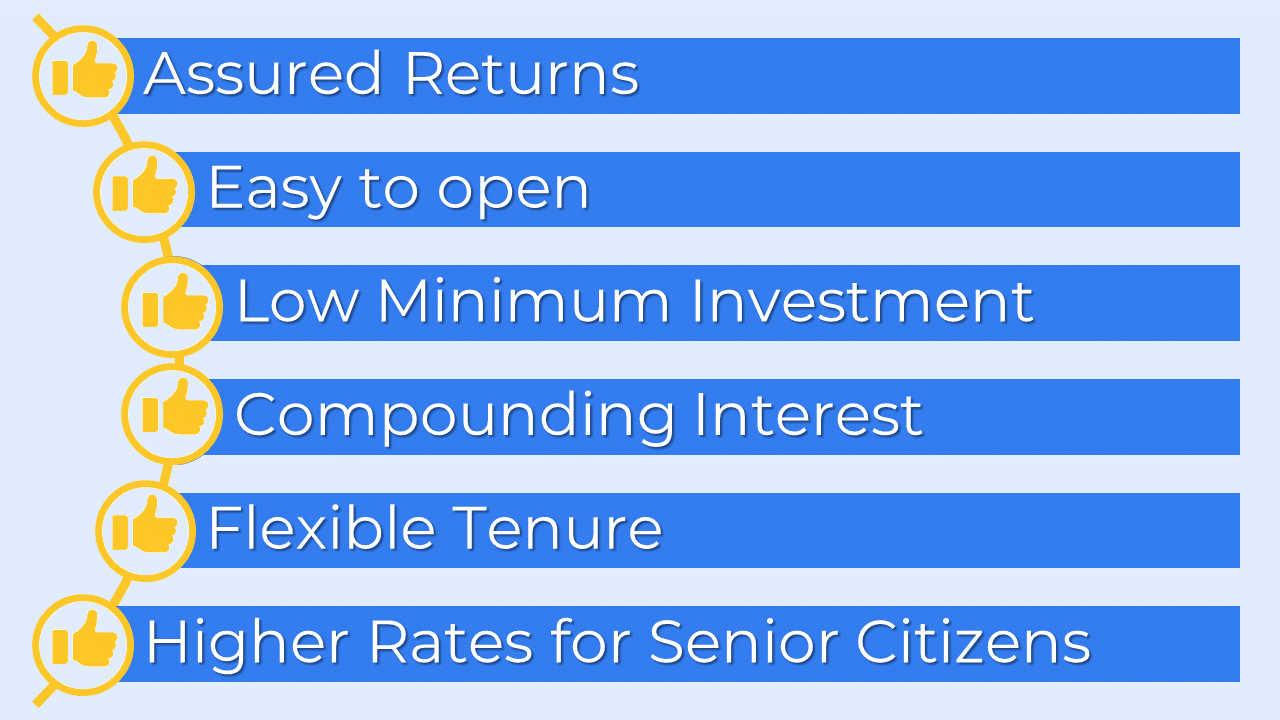
Assured Returns:
Unlike market-linked investments that can be affected by market volatility and potentially result in losses, Fixed Deposits offer a guaranteed rate of return on investments. With FDs, your capital remains secure, and the returns are typically higher compared to savings accounts.
Easy to open:
Opening a Fixed Deposit account is quick and convenient. You can either apply online or visit your nearest bank and request an executive to assist you in opening the account. The entire process can be completed within a matter of minutes.
Low Minimum Investment:
Fixed Deposits are an excellent choice if you aim to cultivate an investment habit but do not have a substantial initial amount. You can begin investing with as little as ₹500/-, making it accessible for small-scale investments.
Compounding Interest:
Cumulative Fixed Deposits offer the advantage of earning interest on interest, allowing for higher returns and accelerated growth of your funds. This means your money multiplies faster over time, resulting in increased earnings.
Flexible Tenure:
You have the flexibility to select a duration ranging from 7 days to 10 years for your Fixed Deposit account.
Higher Rates for Senior Citizens:
Senior citizens can boost their earnings and move closer to a no-compromise retired life by investing in Fixed Deposits.
How to open a Fixed Deposit account online?
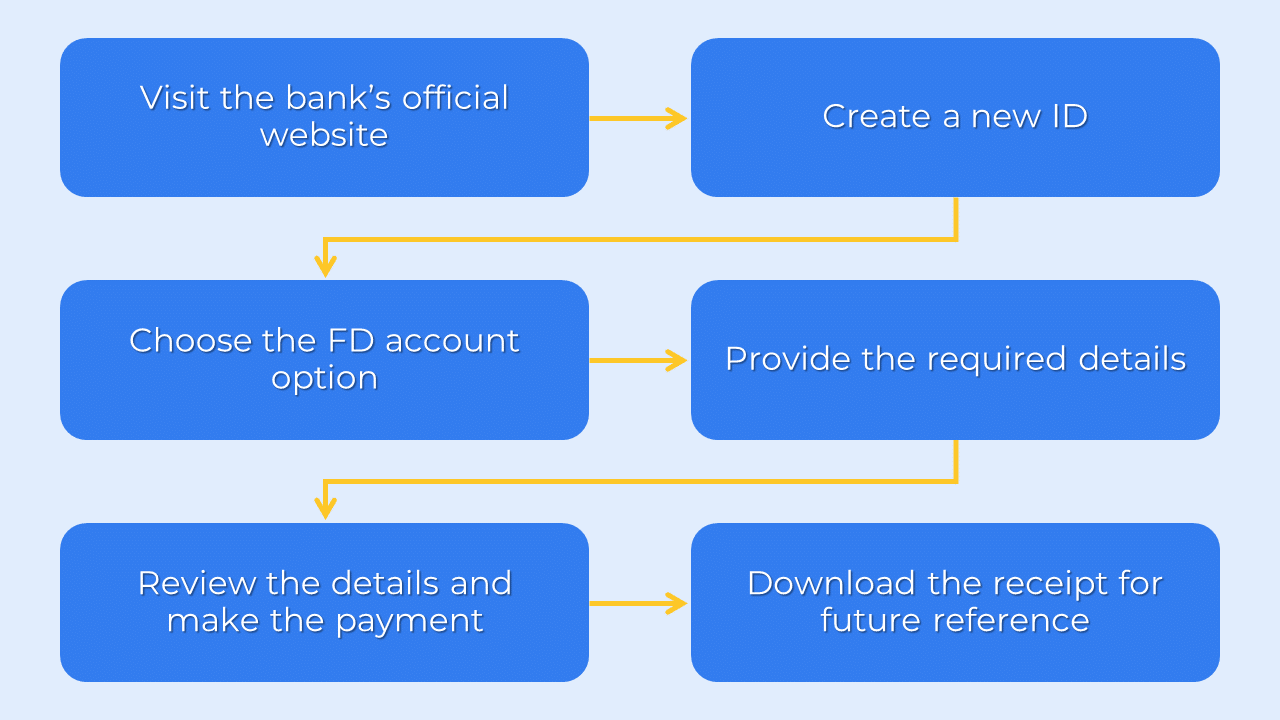
As an investor, you can conveniently open an FD account online and enjoy benefits like easy payment, closure, and renewal. The specific procedure may vary among banks and NBFCs, but here’s a general guide to opening an FD account online:
- Visit the bank’s official website or NBFC, where you wish to open a Fixed Deposit account.
- Create a new ID or log in to your existing account.
- Choose the FD account option.
- Provide the required details, including the principal amount, nominee, tenure, and other necessary information.
- Review and confirm your details, then proceed to make the payment.
- Ensure to download the receipt for future reference.
By following these steps, you can easily open an FD account online and enjoy the convenience it offers.
How to open a Fixed Deposit account offline?
You enjoy the flexibility to open a Fixed Deposit account in any bank of your preference, irrespective of whether you are an existing account holder or not. The process for opening an FD account remains consistent regardless of your existing banking relationship. Here are the steps involved:
If you have an existing account with the bank: Fill out the FD application form provided by the bank. Submit the completed application form to your branch.
If you do not hold an account with the bank: You will be required to submit identity proof, address proof, and other necessary documents to fulfill your KYC (Know Your Customer) requirements along with the FD application form.
By following these steps, you can smoothly open an FD account, regardless of whether you are an existing account holder or a new customer.
How to calculate interest on Fixed Deposit?
Interest on an FD can be calculated using Compound Interest (CI) Formula and Simple Interest (SI) Formula. Banks may use either method based on the deposited amount and tenure.
Simple Interest (SI) can be computed using the formula:
SI = (P × R × T) / 100
Where P represents the principal amount, R denotes the interest rate, and T signifies the time period in years.
For example, if Mr. Kumar invests ₹10,000 at 6% p.a. for four years, he can calculate the interest using the SI formula:
SI = (10,000 × 6 × 4) / 100 = ₹2,400
Compound Interest (CI) can be computed using the formula:
CI = P {(1 + i/100)^n – 1}
Where P is the principal amount, i is the interest rate, and n is the number of years.
For example, if Mr. Sharma invests ₹10,000 at 5% p.a. for four years, the interest using the CI formula will be:
CI = 10,000 {(1 + 5/100)^4 – 1} = ₹2,155.06
You can use an online FD calculator to calculate the interest on your FD quickly.
Who can open a Fixed Deposit account?
The following individuals and entities are eligible to open a Fixed Deposit account in India:
- Individuals who are citizens of India
- Non-Resident Indians (NRIs)
- Minors, with parental or guardian consent
- Senior Citizens
- Public or Private companies, Partnership firms, Sole proprietorships
- Registered Societies and Clubs
- Hindu Undivided Family
- Statutory Board or Local Authorities
Who should invest in Fixed Deposits?
Fixed Deposits are a beneficial investment option for the following:
Investors with a Conservative Risk Tolerance:
If you prefer low-risk investments, Fixed Deposits offer higher returns than keeping money in a savings account.
Investors with Short-Term Financial Objectives:
FDs provide assured returns and have low volatility, making them suitable for achieving short-term financial objectives.
Investors Looking to Diversify Portfolio Risk:
Even individuals with a medium-to-high risk appetite can benefit from allocating a portion of their funds to fixed deposits. This helps balance the risk associated with market-linked instruments like equity or mutual funds.
Retired Individuals Seeking Financial Stability:
For retirees, investing in Fixed Deposits ensures stability and reliability in their investment portfolio, providing a steady income stream.
Overall, Fixed Deposits serve as an attractive investment option for individuals seeking lower risk, stability, and the fulfillment of short-term financial goals.
Fixed Deposit Taxation:
The returns on Fixed Deposits (FDs) are taxable under the provisions of the Income Tax Act of 1961. Here are some important points to note regarding the taxation of FDs:
Taxation on interest earned: The interest accrued on FDs is considered “income from other sources” and is taxed based on the investor’s applicable income tax slab.
TDS (Tax Deducted at Source): If the total interest earned on the FD exceeds ₹40,000 for individuals (excluding senior citizens), banks deduct 10% TDS when the interest is credited to the investor’s FD account. For senior citizens, the threshold amount is ₹50,000.
TDS exemption below threshold: No TDS will be deducted if the total interest earned on the FD is below ₹40,000 (or ₹50,000 for senior citizens). However, the interest income will still be taxable as per the investor’s income tax slab.
PAN (Permanent Account Number) requirement: If your interest income from FDs exceeds ₹40,000/-, you must provide your PAN details to the bank. Failure to furnish PAN may result in a higher TDS rate of 20% on the interest amount, with the earnings being subject to taxation as per the applicable income tax slab.
Please note that the above information is subject to change in accordance with prevailing guidelines and regulations. It is advisable to consult a tax professional or refer to the latest tax laws for accurate and updated information regarding the taxation of FD returns.
Things to remember before investing in Fixed Deposits:
- It is important to exercise caution when dealing with financial institutions offering unusually high-interest rates on Fixed Deposits. Such institutions may pose a risk to your invested capital.
- Avoid the habit of prematurely withdrawing your Fixed Deposit. Early withdrawals can impede the process of wealth creation and hinder the benefits of compounding.
- In case of urgent financial requirements before the Fixed Deposit matures, consider opting for a loan against your Fixed Deposit.
- Additionally, if you do not require the funds immediately upon maturity, it is advisable to renew the Fixed Deposit. Adopting this approach can effectively foster long-term wealth generation for yourself and your family.
Resources:
https://groww.in/calculators/fd-calculator
https://www.bankbazaar.com/fixed-deposit-rate.html
Frequently Asked Questions:
What are the minimum and maximum deposit amounts for Fixed Deposits?
The minimum deposit amount required for FDs varies among different banks. However, there is generally no maximum limit on the amount invested in an FD.
What is the minimum age requirement for opening a Fixed Deposit?
An FD can be opened for a minor. However, in the case of minors, a parent or guardian must open the FD on their behalf. Any individual who is 18 years or older can independently open their own FD account.
What documents are required for Fixed Deposit?
You will be required to furnish the following documents to initiate a fixed deposit account opening.
Passport
Driving license
Proof of possession of Aadhaar number
Voter’s Identity Card issued by the Election Commission of India
Job card issued by NREGA, signed by a State Government officer
Letter issued by the National Population Register containing name and address details
How frequently will I receive interest on my Fixed Deposits?
The frequency of interest payments on your Fixed Deposits depends on your chosen FD plan. You have the flexibility to opt for Monthly, Quarterly, or Annual interest receipts. Alternatively, if you opt for the reinvestment option, the interest will be compounded and reinvested together with the principal amount. Consequently, you will receive the total accumulated amount upon maturity.
What happens if I wish to withdraw my Fixed Deposit before the maturity date?
In case of emergencies, most banks provide the option to liquidate your FD prematurely. However, please note that early withdrawal typically incurs a small penalty charge and the forfeiture of interest for the remaining duration of the FD. It’s important to be aware that premature withdrawal is generally not permitted for tax-saving FDs.
Can I transfer my Fixed Deposit to another branch or bank?
Fixed deposits can be transferred from one branch to another within the same bank. To initiate the transfer, you need to contact the bank branch manager where your FD was originally started. Submit a written request for the transfer along with the FD receipt. After the account is verified, your FD will be transferred to the requested branch.
However, it’s important to note that a Fixed Deposit account cannot be transferred from one bank to another. If you wish to move your FD to a different bank, you will need to prematurely close the FD from your current bank and open a fresh FD with the new bank.
How can I avail exemption from TDS for Fixed Deposits?
Individuals whose interest earnings from FDs are below ₹40,000 per annum (₹50,000 for senior citizens) can avail TDS exemption. To avail this exemption, investors can submit Form 15G, while senior citizens will need to submit Form 15H. These forms allow individuals to declare that their income from FD interest is below the taxable limit, thereby requesting the bank not to deduct TDS on their interest earnings.
What should be done in case the account holder passes away before the maturity date?
In the event that the account holder is deceased before the maturity date, the nominee can step forward and claim the maturity amount. However, if the investor did not designate a nominee, the family members of the deceased will need to provide a succession certificate or legal heir proof to claim the maturity amount.
What is an FD nomination?
An FD nomination refers to the process in which the account holder appoints a nominee. The nominee is chosen to ensure that in the event of the account holder’s demise, the maturity amount of the FD can be claimed and withdrawn by the nominee.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, Fixed Deposits are a secure and reliable investment option that offers assured returns and a range of benefits. By understanding the various types of Fixed Deposits, eligibility criteria, taxation aspects, and the process of opening an FD account, individuals can make informed decisions to achieve their financial goals while preserving their capital.
Thank you for taking the time to read this article. Should you have any questions, please feel free to Contact Us.
Disclaimer:
This article provides general information only and does not constitute financial advice. Financial regulations, product terms, and industry guidelines are revised from time to time. While we have made efforts to ensure the accuracy of the information presented, we do not guarantee its completeness or accuracy. We disclaim any liability for loss or damage arising from actions taken based on the information provided in this article. To make informed financial decisions, please do your own research and consult with a qualified financial professional.
SPREAD THE WORD WITH YOUR NETWORK

